PLATFORM SIMPAC¶

SIMPAC developped by ARIA Technologies is a 3D SaaS platform design for assessing dispersion of accidental releases.
SIMPAC Full SaaS platform embeded the PMSS 3D software for assessing risks arising from the dispersion of toxic industrial gases (storage accident, pipe failure, fire). It can be incorporated in an alert system, outputs maps of forecast concentration …
The urban environment is more and more widespread. Fields and forests are mixed with more or less densely populated residential areas. The important droughts increase the risk of forest fires and the propagation of a forest fire towards the residential areas. To meet the need for risk assessment, the SIMPAC platform now integrates the FARSITE forest fire propagation model to estimate the burned areas and the amount of pollutants released by the fire.
This documentation is intended for users. It recalls the principle and the functioning of the SIMPAC platform.
The documentation also lists the steps to follow for modeling an industrial incident.
The theoretical training is divided into 2 parts and the documents can be downloaded
here and the rest here.
The Origins of Aria and SIMPAC¶
ARIA Technologies
Since its foundation in 1990, ARIA Technologies is fully dedicated to the study of the atmospheric environment. Technics and softwares implemented for the different studies are widely approved and regarded by the French DREAL and Ministries.
ARIA Technologies has been developing stimulation technologies, constantly improved, that it owns. Its team, composed of air quality’ specialists and scholars in environment, ensures the drafting of modelling systems, their applications, and the exploitation of the results to wholly satisfy the clients’s demands. Therefore, ARIA Technologies offers two complementary approaches to its clients : the conception and the development of simulation systems, with a service of studies and expertise.
ARIA Technologies commercialises the softwares that have been developed exclusively by the company. The users of the ARIA softwares work in different fields: manufacturers, French local district administrations and national administrations, consultancy firms, or scholars. The first generation of SIMPAC was developed by ARIA Technologies for Atmo Sud, as part of the “Force d’Intervention Rapide” (the Prompt Intervention Force), created by 3 AASQA: Atmo Normandie, AuRA and AtmoSud.
Models used in SIMPAC¶
PMSS
ARIA/ARIANET in collaboration with CEA has developed the PSWIFT & PSPRAY models in the Parallel-Micro-SWIFT-SPRAY (PMSS) system. The PSWIFT model is a mass-conserving diagnostic atmospheric model. The PSPRAY model is a 3D stochastic Lagrangian dispersion model of pollutants in the atmosphere.
Farsite
The FARSITE model is widely used around the world to model fire spread. The FARSITE model is developed by the Missoula Fire Sciences Laboratory. It is integrated into the operational tool Flammap. FARSITE is a forest fire propagation model, which integrates models of surface fire, crown fire, fire acceleration by brandons with consideration of Fuel moisture.
General Information¶
The SIMPAC platform has been designed according to the four following aims:
To modelize the impact of an industrial incident and accident, within the following first hour,
To easily modelize variations,
To easily produce exploitable results,
To be easily exploitable by people that are not specialist of atmospheric modelling.
To implement these purposes, the SIMPAC platfom:
Integrates several configurations of PMSS dispersion models, of various complexities, to ensure the adaptation to any issues that must be treated, from factories’ scale to a whole urban area of region.
Completely functions through a Web Graphic User Interface (Web GUI) accessible from any web browser.
Important
The SIMPAC platform is optimized for Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge and Firefox.
The SIMPAC platform enables two types of modelling:
A direct mode of pollutants’ s dispersion, with three configurations and increasing computational times:
plumes’s trajectories,
dispersion with unitary sources,
cartography of the dispersion of pollutants.
An inverse mode for the origin of plumes of pollutants, with two configurations and increasing computational times:
retro-trajectory of the pollutant plumes,
cartography of the retro-dispersion of pollutants and estimation of the source location.
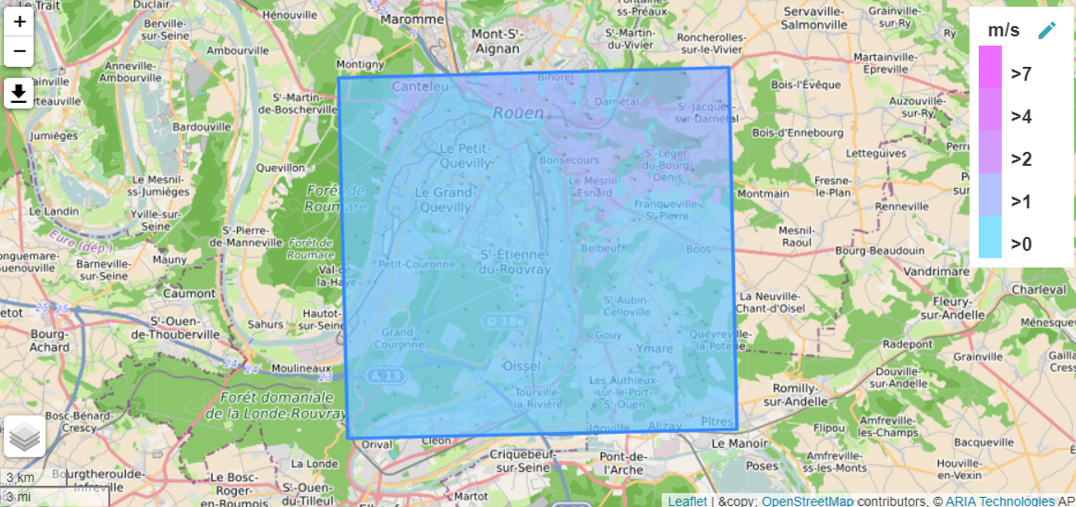
Results displayed on the SIMPAC platform Atmo Normandie¶
General documentation
Meteorological modellings
Dispersion modellings
Forest fire & Dispersion modellings